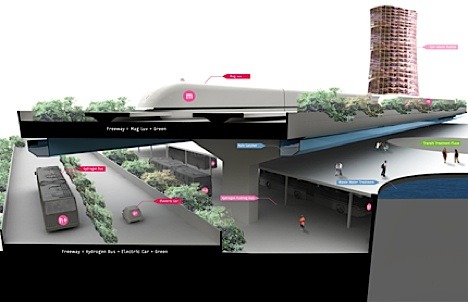
Design schools are starting to tackle questions of urban scale city design in their masters programs. The key to future transit systems is to make that form of travel the best it can possibly be. Ask, what would make people choose this form of transport over other alternatives if they had many equally accessible and affordable options? Why might they want to travel this way? What would be unique, good or special about the experience?
Densification of urban landscapes
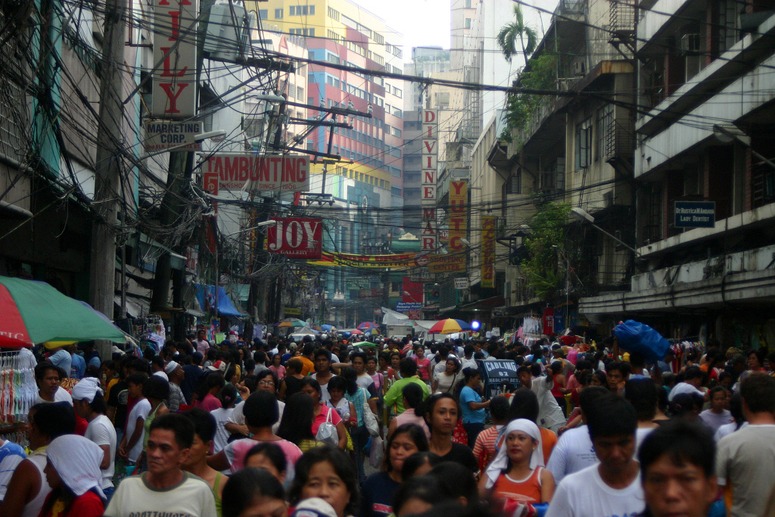
Jonathan Solomon tells a CNN inverviewer that ‘Dense cities use less energy per person than more dispersed suburban equivalents. When you consider a city in relation to its larger region, the ecological footprint per person in a city may be significantly smaller than rural inhabitation’. Similarly, public transport systems use less land than private cars. So it is likely that if we must make our cities more sustainable then we must adopt densification policies. The main possibilities include: make more use of airspace (eg by building higher); make more use of underground space (eg for transport and parking); make more use of waterspace (eg with houseboats, tunnels etc); make better use of roofspace (eg for parks and gardens); make better use of ‘space between buildings’ (eg with new structures, cantilevers, balconies etc). In comparison with Tokyo, London is a very low density capital, and profligate with its use of transport space. The urban density in London (5,000/km2) is one eigth of the density of Manila.
OK, but all these measures require ingenuity and design imagination. They require studies from urban designers and landscape architects to discover how densification can take place in conjunction with improvements to the quality of life in cities. And we should remember the sceptics, like Jan Gehl, who argue that low density cities are more sustainable. My instinct is that there is no ‘one right answer’: cities need high density nodes with lower density peripheries.
Above image courtesy Jake Hirsch-Allen
Will we live to see the End of Suburbia?
The beginning or the end of the car?
Is peak oil, sustainability and climate change the beginning or the end of the car as we know it? With the advent of modernism carparks became first part of a highrise building to be constructed and were considered as part of the foundation system. There are a number of concerns with parking in urban areas. Will pollution and noise issues be meet by electric cars? Will innovative greened multistacking carparking arrangements be proposed for multi-density dwellings? How will congestion be addressed?
How will car supply and demand issues be thought about? Should urban residences be carfree with the possibility of outer-urban garaging accessible beyond the urban core area? Should urban work and commuting also be limited to the periphery of the inner-core? If so, who should be able to access this inner centre by car? Why?
Will eco-traffic engineers be engaged to design flow throughs and do capacity modelling for all new development sites so that designers can innovate and demonstrate best practice? Who will dream of the transit and traffic organisational schemas of our new cities?
More questions than answers!
Re: cycling It is Cost Effective
What is needed to induce the die-hard city commuters to leave behind their cars and adopt cycling as a mode of transport? Should the cost of using the car in central city areas be so cost prohibitive that only the those willing to part with large sums for the privilege persist? Or should urban designer adopt a range of innovative measures to entice inner city commuters to adopt what is afterall a healthier lifestyle alternative?
The McDonalds Cycle Centre in Chicago’s Millenium Park is leading the way in rethinking what it means to cycle and the sort of facilities which may transform the way commuting and recreational cycling is viewed. Philip Modest Schamberlan and + Anton Fromm’s Bicycle Hotel intends to entice the cyclist into the mountains in pursuit of a recreational touring lifestyle by providing an intriguing Fractal experience perched above Lake Garda.
Gardening on the dole: workfare, punishment or pleasure?
 The Daily Mail reports that under a UK government policy announced yesterday ‘the feckless unemployed will be forced to take part in a punishing US-style ‘workfare’ scheme involving gardening, clearing litter and other menial tasks’. It is a bad account of what could be a good policy. Giving people money for doing something is better than giving them money for doing nothing. Work is not a punishment; it is what the world does. But gardens already suffer from a skill shortage and gardening is not a ‘menial task’ and it should not be assumed that the unemployed are feckless or unskilled. Many over 40s know about gardening and lose their jobs because of market conditions or bad management. Surely it is healthier and more pleasurable to work as gardeners, or to help for elderly people living at home, or similar, than to get the dole and watch TV.
The Daily Mail reports that under a UK government policy announced yesterday ‘the feckless unemployed will be forced to take part in a punishing US-style ‘workfare’ scheme involving gardening, clearing litter and other menial tasks’. It is a bad account of what could be a good policy. Giving people money for doing something is better than giving them money for doing nothing. Work is not a punishment; it is what the world does. But gardens already suffer from a skill shortage and gardening is not a ‘menial task’ and it should not be assumed that the unemployed are feckless or unskilled. Many over 40s know about gardening and lose their jobs because of market conditions or bad management. Surely it is healthier and more pleasurable to work as gardeners, or to help for elderly people living at home, or similar, than to get the dole and watch TV.
Style Conscious
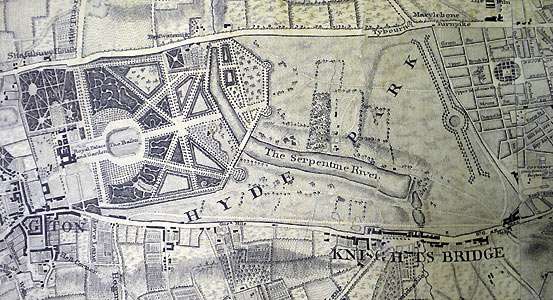
In 1730 Queen Charlotte ordered the damming of the Westbourne River as part of a general redevelopment of Hyde Park and Kennsington Gardens by Charles Bridgeman. The Serpentine Lake in Hyde Park is the remnant of the Westbourne River which since 1850 has been diverted into a culvert and runs into the Thames near Chelsea. “The Serpentine Lake was one of the earliest artificial lakes designed to appear natural” and was widely imitated. The Long Water because of its relatively undisturbed nature is a significant wildlife habitat.
Hyde Park and its surrounds has changed considerably since its inception. Contextualising the statute of Achilles by Richard Westmacott which was said to have originated in the classical taste of the Countess Spencer, demonstrates the remarkable changes that have taken place both in the use of the park and in the urban environment which surrounds it. The Queen and Prince Albert are drawn taking air in their carriage as they pass by the statute c1840.
Achilles meanwhile remains a most admired archetypical hero.