More design (cities, architecture, landscapes, gardens etc) should be more context-sensitive:
More design (cities, architecture, landscapes, gardens etc) should be more context-sensitive:
- it is more sustainable (less energy, local plants, local materials etc)
- traditions which have survived what Christopher Alexander calls ‘an endless period of time’ are likely to be adapted to local cultural and geographical circumstances
- local character is what local residents usually want
- local character is what tourists usually want
I am NOT however arguing against innovation, which local people and tourists can all appreciate. I am arguing that every design team MUST explain and MUST justify the contextual approach they have adopted. Similarity, Identity and Difference are all welcome in the right circumstances. Garden travel is one of life’s great pleasures – and it helps one see that Russian design should not be copied in China, French design should not be copied in Russia, American design should not be copied in Dubai, British design should not be copied in India, Japanese design should not be copied in America, etc etc etc. Mobile phones and cameras are international go-anywhere products. Designed gardens and landscapes should have local roots, however much they learn from elsewhere. Curiously, designers often understand this best when working outside the countries in which they were born.
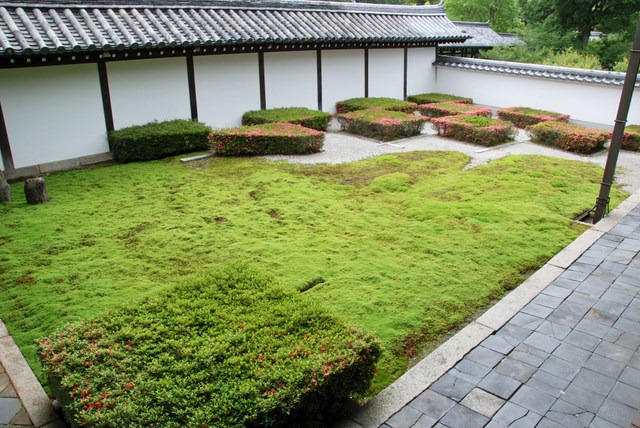
The photograph is of the garden in Bundi where Rudyard Kipling wrote Kim, and possibly wondered:
Winds of the World give answer! They are whimpering to and fro
And what should they know of England who only England know?