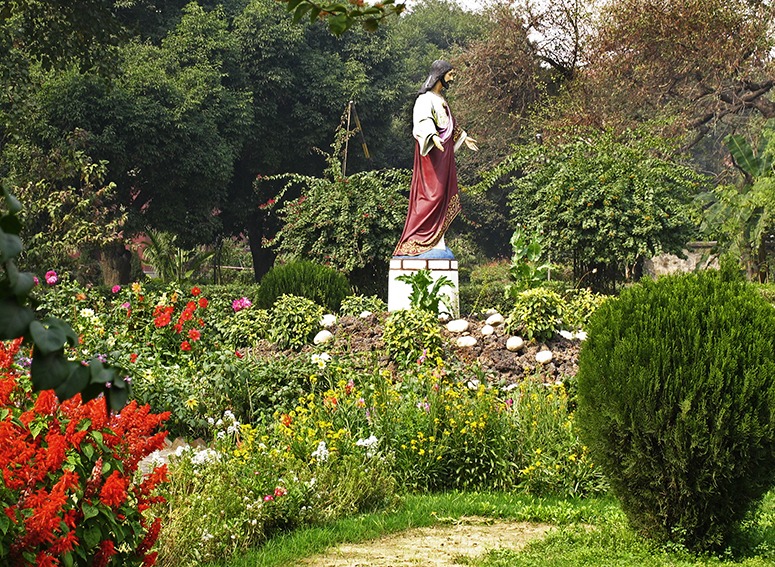
This Christian symbol, in the garden of a chuch in India, is pleasing - and startling: it highlights the LACK OF CHRISTIAN SYMBOLS in European gardens, be they sacred or secular.
Ian McHarg, the most influential landscape architect of the twentieth century, criticised the Book of Genisis for giving man dominion over our planet’s animials and plants ‘And God said, Let us make man in our image, after our likeness: and let them have dominion over the fish of the sea, and over the fowl of the air, and over the cattle, and over all the earth, and over every creeping thing that creepeth upon the earth.’ (Genesis 1:26) McHarg, following Lynn White, saw this as a Biblical basis for not recognizing rights in non-human life. McHarg thought it was a reason for Christians not identifying an ethical duty to conserve the environment, biodiversity or ‘wild nature’. Forests, for example, which were associated with paganism, need only be conserved if, as part of their ‘dominion’, humans make this choice in their own interest. Aldo Leopold, who trained as a forester, argued that humanity should adopt a ‘land ethic’.
Christian Ecologists have responded by interpreting ‘dominion’ as ‘stewardship’. I see this as an incomplete re-interpretation of the Bible, because a steward takes instructions from a lord. A steward is ‘An official who controls the domestic affairs of a household, supervising the service of his master’s table, directing the domestics, and regulating household expenditure; a major-domo’ (OED). A steward would have a duty to conserve the environment only if the lord issued such a command. The etymology of steward is ‘most probably Old English stig a house or some part of a house’ (OED)
But what of Christianity and garden design? There is a Biblical injunction to grow food ‘…and thou shalt eat the herb of the field; In the sweat of thy face shalt thou eat bread, till thou return unto the ground; for out of it wast thou taken: for dust thou art, and unto dust shalt thou return.‘ But, as the magnificent words of the King James Bible testify, growing food was more of a duty a pleasure. Then, when Christianity became the official faith of the Roman Empire, the injunctions against idolatry (eg in the First and Second Commandments) came to the fore:
1. Thou shalt have no other gods before me.
2 Thou shalt not make unto thee any graven image, or any likeness of any thing that is in heaven above, or that is in the earth beneath, or that is in the water under the earth. Thou shalt not bow down thyself to them, nor serve them: for I the LORD thy God am a jealous God, visiting the iniquity of the fathers upon the children unto the third and fourth generation of them that hate me.
Rome’s public places, and Roman gardens, had been rich in statues of pagan Gods. After Christianity was declared the official religion of the Roman Empire, by Theodosius I on 27 February 380, these statues came to be regarded as idols and graven images. So they were removed or destroyed. This was a blow to the classical tradition of garden design, though not to the practice of gardening. Christian monks became expert gardeners and cloister garths are widely interpreted as examples of sacred geometry – as symbols of God’s perfection. The Vatican has great gardens but they do not have Christian symbols. The gardens of Lambeth Palace are sadly neglected. Some cloisters, like Salisbury, have had wholly inappropriate designs. Other cloister garths (eg Certose di Pavia) have parterre designs – which are not Christian symbols.
During the renaissance period, ‘graven images’ re-appeared in gardens. This was an aspect of what is called ‘renaissance paganism’. The Belvedere Court, in the heart of the Vatican, had the greatest collection of pagan sculpture in all Europe. I do not know of a contemporary justification for their presence but the argument seems to have been that since there is only one creator god, he must have created the pagan gods – and so they could be used to symbolise the Christian virtues. Venus is the prime example. Seen as a symbol of Love, she became an excellent reason for placing statues of nude girls in gardens. Protestants seem to have been less confident about her presence, as they were about other ornament and decoration, but even the Baroque gardens of the Counter-Reformation allowed for the siting of graven images in gardens, with two qualifications: they had to be pagan symbols and they could not, of course, be worshiped. It is odd that statues of pagan gods were allowed but statues of the Christian God, Jesus, Mary and the Apostles were not allowed. Should this policy be re-considered? Yes. Representations of the Holy Family are allowed in Christian art – so why should they be banned in Christian gardens? I look forward to the English churches helping to organise the sponsorship of Christian Gardens at the Chelsea Flower Show and as part of the Chelsea Fringe so that they can be kept as features of London’s garden heritage. Also, there is significant scope for improving the management of the gardens associated with cathedrals and churches. These projects would be demonstrations of new life in old institutions. There is a particular opportunity to use flowers of special importance to Christians, including red roses, white lilies and ‘flowery meads’.
[Note: the relationship between Christianity and gardens is discussed in British Gardens: History, philosophy and design London:Routledge 2013 p.148ff]