[Note: the folks who plonked the tent in front of the Opera House were plonkers].
(Image courtesy Dave Keeshan)
(Image courtesy Dave Keeshan)
It is always a challenge when considering heritage how to respect the past while accommodating the new. The houtongs in Beijing are now facing the predicament of a modernising city. Traditional society and lifestyles have changed. Consumer demands are different.
So the traditional courtyard house is being reinterpreted…and in some instances modernism and tradition are facing each other quite literally.
However, there is much to be gained from understanding the tradition of the courtyard house and the patterns of life which gave rise to it. The garden of the courtyard house seems to have been predominantly a place for trees.. but perhaps also for lawn?
I despair of the archaeologists who manage historic gardens – please can someone cheer me up by pointing to some good examples of garden archaeology combined with garden management. (Photograph of Herculaneum courtesy dandwig)
The best garden archaeologists, like those who ‘restored’ Kenilworth Castle Garden, seem to be dry academics devoid of design sense or design judgment. Normal, bad, garden archaeologist-managers seem to work on the principle that ‘we don’t know much about historic gardens so they must have resembled modern gardens’. Gertrude Stein remarked that ‘Civilization begins with a rose. A rose is a rose is a rose is a rose.’ GERTRUDE STEIN DID NOT say “Civilization begins with a garden. A garden is a garden is a garden is a garden.” Garden archaeologist-managers reason that because modern gardens have lawns and shrubs THEREFORE historic gardens must have been the same. It is rubbish and their approach to garden management is rubbish.
Take Roman peristyle gardens as an example. I know of many fresco paintings of Roman garden planting, always with flowers and birds, but not one single example of an illustration of a Roman lawn. So why do our garden archaeologists supply all excavated Roman gardens with lawns? Are they vandals, penny-pinching accountants or imbiciles?
Roman courtyard gardens DID NOT have mown lawns and the Romans DID NOT have lawn mowers. They clipped box, to make what we call topiary, but there are very few illustrations of linear and uniform box hedging of the type which became common in renaissance gardens. Nor are there any illustrations of Roman parterres – and I am doubtful about the accuracy of Barry Cunliffe’s ‘restoration’ of the garden at Fishbourne Roman Palace
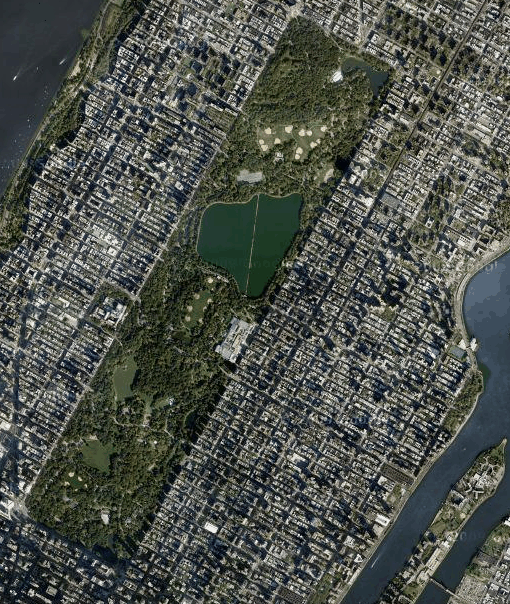 It is interesting to see parks within their urban setting to start to understand the relationship between urban fabric and parkland. Apparently Olmsted‘s Central Park faced something of a crisis in the 1970s and was revived in the 1980s through a major restoration project.
It is interesting to see parks within their urban setting to start to understand the relationship between urban fabric and parkland. Apparently Olmsted‘s Central Park faced something of a crisis in the 1970s and was revived in the 1980s through a major restoration project.
So the times change and people demand new things of their parks? After the French Revolution fortuneately the true value of Versailles was recognised…So hopefully designers and the public will be able to recognise the value of the past when refurbishing green spaces for the future.
I am the enemy you killed, my friend.
I knew you in this dark: for so you frowned
Yesterday through me as you jabbed and killed.
I parried; but my hands were loath and cold.
Let us sleep now…’ (Wildrid Owen Strange Meeting)
Image courtesy jscolman – with added blood See also: Ghostcycle.org
My winter post on White Commuting has led me to the following classification:
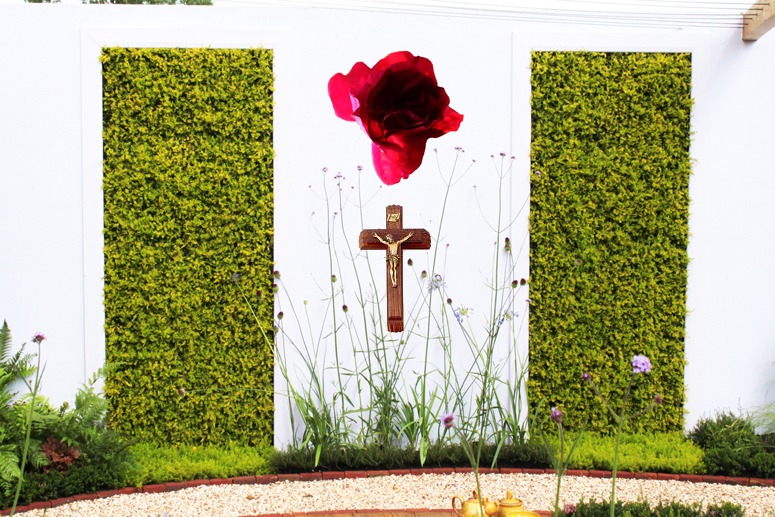

The green walls being made in gardens have more significance as symbols than as practical contributions to sustainability
Garden designs can communicate with words and images – or they can continue with the silence of abstract modernism.
The drift from modernism to postmodernism continues, but with little knowledge and less thought. A recent post on The Fower Sermon, recalled that the dying Buddha used a single flower to speak volumes. He also advised: “All conditioned things are impermanent. Work out your salvation with diligence.” Christianity has been more concerned with relationships between humans than with the HUMANITY:ENVIRONMENT relationship.
During Europe’s Middle Age, the Rose was an eloquent Christian symbol. The five petals of the rose symbolised the five books of Moses (the Pentateuch), the five wounds of Christ and other pentads. Gazing at a rose, the garden owner could feel inspired and re-assured, as when remembering a famous quotation, a line of poetry, a proverb or the heroic deed of a saint or martyr.
So are there symbols of comparable power for current garden designers to explore? I think many green roofs and green walls fall into this category. Presently, they have more value as symbols than actual contributions to sustaining life on earth. I make no complaint about this – but am deeply skeptical about any practical contribution they might make to saving the planet from climate change, forest clearance, rising sea levels, interruption of the Atlantic heat conveyor – or sin. And if green walls use electric pumps they aggravate the risks we face.